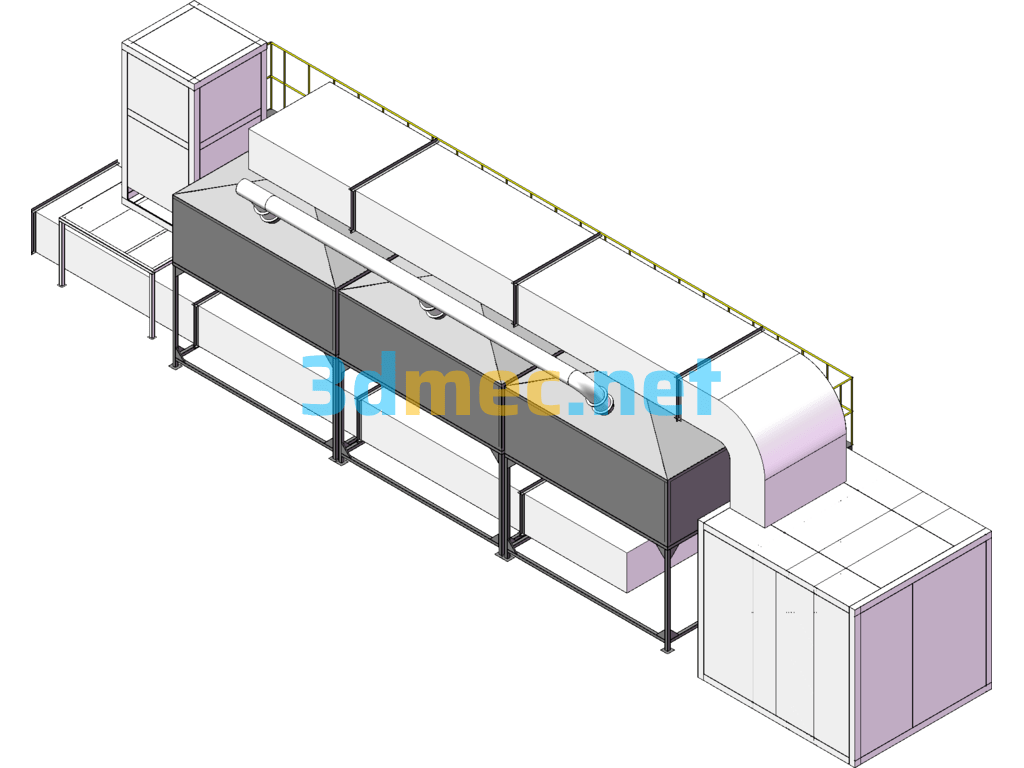
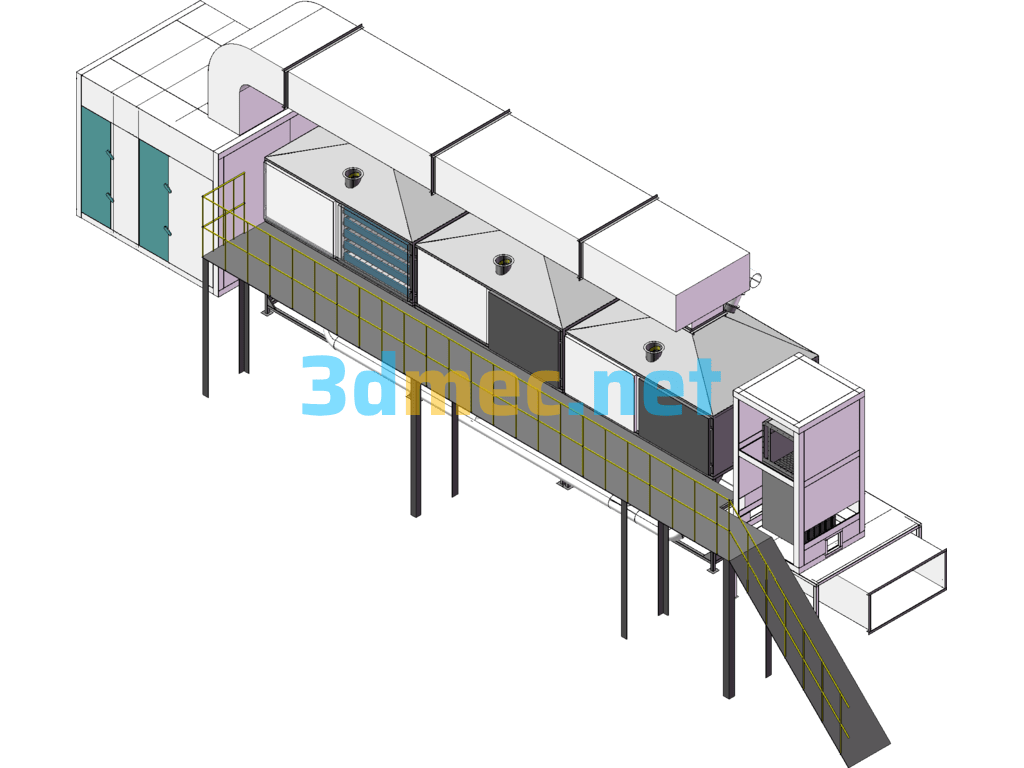
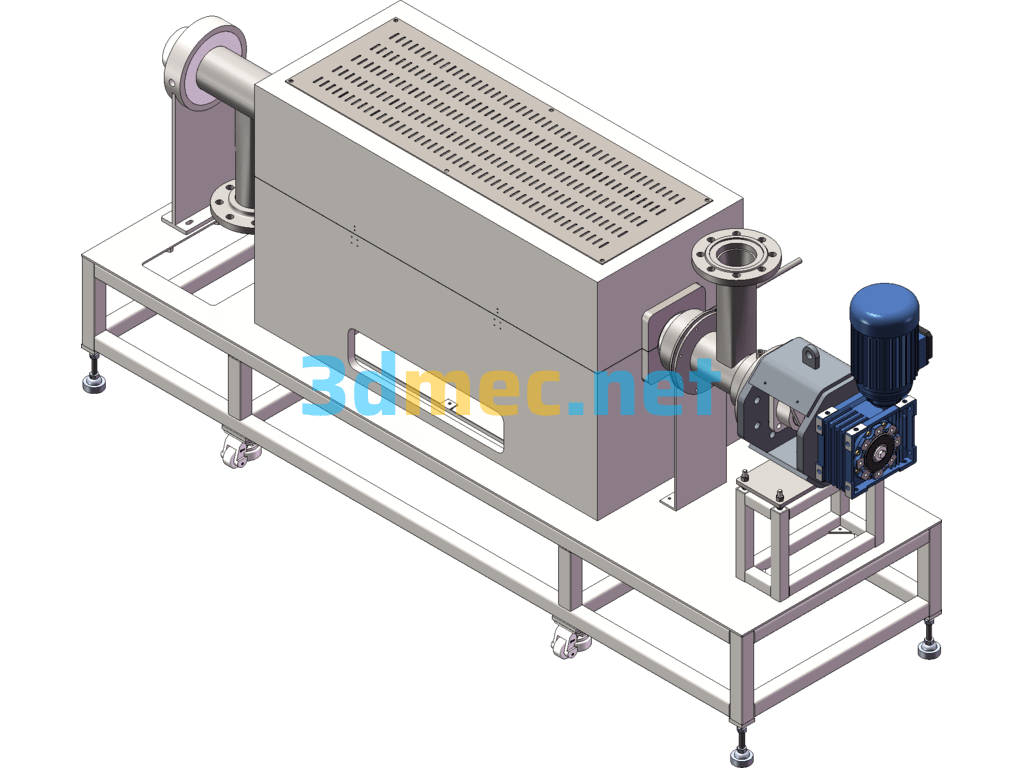
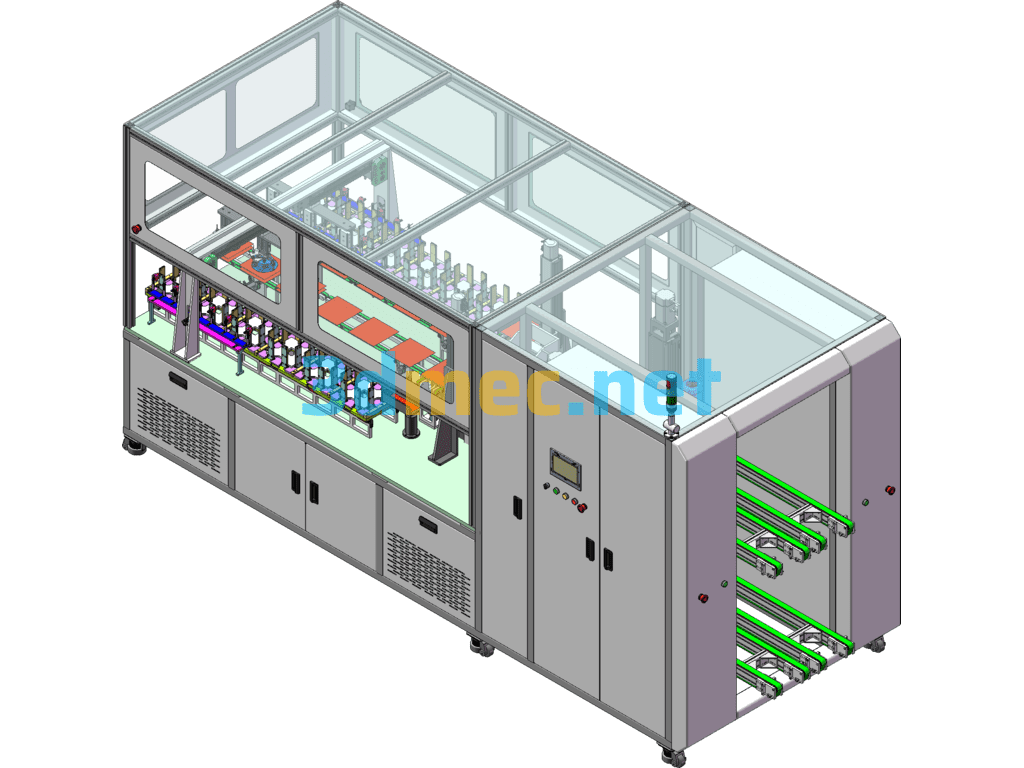
RCO Activated Carbon Adsorption Catalytic Combustion Equipment – 3D Model SolidWorks
Activated carbon adsorption technology has been used in the domestic pharmaceutical, chemical and food industries for many years. It has been used for industrial wastewater treatment since the 1970s. Production practice shows that activated carbon has excellent adsorption for trace organic pollutants in water. It has good adsorption effect on industrial wastewater such as textile printing and dyeing, dye chemical industry, food processing and organic chemical industry. In general, it has unique removal ability for organic matter in wastewater represented by comprehensive indicators such as BOD and COD, such as synthetic dyes, surfactants, phenols, benzene, organic chlorine, pesticides and petrochemical products. Therefore, activated carbon adsorption has gradually become one of the main methods for secondary or tertiary treatment of industrial wastewater. Adsorption is a slow process in which a substance adheres to the surface of another substance. Adsorption is an interfacial phenomenon, which is related to the change of surface tension and surface energy. There are two driving forces that cause adsorption, one is the repulsion of solvent water to hydrophobic substances, and the other is the affinity and attraction of solids to solutes. Adsorption in wastewater treatment is mostly the result of the combined action of these two forces. The specific surface area and pore structure of activated carbon directly affect its adsorption capacity. When selecting activated carbon, it should be determined by testing according to the water quality of the wastewater. For printing and dyeing wastewater, it is advisable to select carbon with developed transition pores. In addition, ash content also has an effect. The smaller the ash content, the better the adsorption performance; the closer the size of the adsorbate molecule is to the carbon pore diameter, the easier it is to be adsorbed; the adsorbate concentration also affects the adsorption capacity of activated carbon. Within a certain concentration range, the adsorption capacity increases with the increase of the adsorbate concentration. In addition, water temperature and pH value also have an effect. The adsorption capacity decreases with the increase of water temperature and increases with the decrease of pH value. Therefore, low water temperature and low pH value are conducive to the adsorption of activated carbon. Activated carbon desorption is the reverse process of adsorption. It is an operating process in which the adsorbed components are saturated and precipitated from the adsorbent, and the adsorbent is regenerated. That is, the process in which the substance adsorbed on the interface escapes the interface and re-enters the bulk phase under certain conditions, which is also called desorption. Activated carbon regeneration is the reactivation of activated carbon saturated with adsorption after being treated under certain conditions. Activated carbon has been widely used in environmental protection, industry and civil use, and has achieved considerable results. However, after the activated carbon is replaced due to adsorption saturation, the use of activated carbon adsorption is a physical process. Therefore, high-temperature steam can be used to desorb impurities in the used activated carbon and restore its original activity to achieve the purpose of reuse, which has obvious economic benefits. The regenerated activated carbon can still be reused and regenerated continuously. Activated carbon regeneration is the reactivation of adsorption saturated activated carbon after being treated under certain conditions.
Specification: RCO Activated Carbon Adsorption Catalytic Combustion Equipment – 3D Model SolidWorks
|
User Reviews
Be the first to review “RCO Activated Carbon Adsorption Catalytic Combustion Equipment – 3D Model SolidWorks”
You must be logged in to post a review.





There are no reviews yet.